Golem Python Quickstart
Introduction
In this article, we'll show you how to run a simple task on the Golem Network using the Python SDK.
We will perform a simple task for the quickstart, which will render six scenes in parallel on rented providers.
It should take just a few minutes to complete, and you will see the generated output files which are PNG images in your folder.
Installing and running Yagna
Yagna is a service that communicates and perform operations on the Golem Network. Let's get started by installing it.
Install Yagna
On Linux/ MacOS, you can install it using our helper script like this:
curl -sSf https://join.golem.network/as-requestor | bash -You might be asked to modify your PATH afterward.
Should you encounter any problems, please reach out to us via our Discord channel or consult the following resource for troubleshooting.
Start the Yagna service
yagna service runRunning the your first task on the Golem Network
Now you have the yagna daemon running, you may proceed with running a task as a requestor.
Create a new project folder:
mkdir yagna-python-tutorial
cd yagna-python-tutorialPrepare a virtual environment for the tutorial script:
python3 -m venv --clear ~/.envs/yagna-python-tutorial
source ~/.envs/yagna-python-tutorial/bin/activateand install the Golem SDK by typing in the command line:
pip install -U pip
pip install yapapiGet the requestor agent's code
Check out or download the yapapi repository:
git clone -b b0.12 https://github.com/golemfactory/yapapi.git
cd yapapiSet the yagna app key
In order for the requestor agent to connect with the yagna daemon, you need to provide it with the previously-generated app key. You do that by setting the appropriate environment variable. Create a new app-key:
yagna app-key create requestorThis should produce a 32-character-long hexadecimal app key that you need to note down as it will be needed to run the requestor agent.
export YAGNA_APPKEY=insert-your-32-char-app-key-hereRun the example
The example we're showcasing here resides in the examples/blender directory within yapapi's codebase so, ensure that you're in the checked-out repository's directory and run:
cd examples/blender
python blender.pyOnce you launch the example, you should see some messages reflecting the progress of your tasks' execution - agreement confirmations, task dispatches and finally task completions.
The example in question generates six discrete tasks for providers to execute so after those six activities are completed and results returned, the whole job is finished.
If everything goes right, after what could be anything from half-a-minute to a few minutes, you'll hopefully see the message announcing the successful completion of your assignment including a short summary of what had happened during the execution, which providers took part in the execution and the accumulated GLM cost of the whole task, e.g.:
Computation finished in 77.5sNegotiated 1 agreements with 1 providersProvider 'odra' computed 6 tasksTotal cost: 0.218290307253
Yay! With this, you have completed your first job as a requestor in the new Golem network!
Output
You can verify that the task is indeed done by examining the generated output files which are PNG images with the selected frames of the rendered animation that should appear in the directory from which you ran the example script (examples/blender within the cloned repository's path if you followed the tutorial precisely) .
Here is an example rendered frame, provided here for reference:
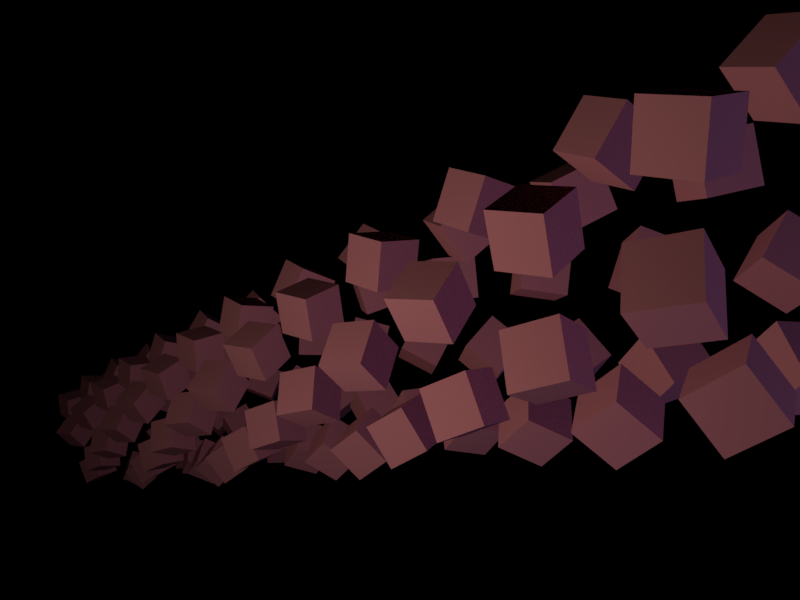
Payments
Finally, you can verify that the providers have been paid for the work they contributed to get that output to you. First, acquire your Ethereum address - you can do that by running:
yagna app-key listThe value in the id column is your the Ethereum address of your yagna node on the testnet. Once you have that address, you can check that the transactions have been sent.